728x90
6.5 사실과 거짓
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int tv, fv;
tv = (1 < 2); // true
fv = (1 > 2); // false
printf("True is %d\n", tv);
printf("False is %d\n", fv);
return 0;
}
Output :
True is 1
False is 0
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = -5;
int j = 5;
while (i)
printf("%d is true\n", i++);
printf("%d is false\n", i);
printf("\n");
while (j)
printf("%d is true\n", j--);
printf("%d is false\n", j);
return 0;
}- 0이면 false고, 그 외의 값들은 모두 true
Output :
-5 is true
-4 is true
-3 is true
-2 is true
-1 is true
0 is false
5 is true
4 is true
3 is true
2 is true
1 is true
0 is false
6.6 _Bool 자료형
- 대부분의 사람들이 내부적으로 bool type을 만들어 사용하고 있었으므로 그와의 충돌을 위해 이름 앞에 _를 붙이고 첫 글자를 대문자로 함
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i;
//while (i = 5) {statement} // i에 5를 대입한 후, 조건문 안의 값이 5이므로 true -> statement 실행
//
//while (i == 5) {statement} // i의 값이 5인지 확인
_Bool boolean_true = (2 > 1); // true. C언어에서는 _Bool 자료형도 정수형으로 처리
_Bool boolean_false = (1 > 2); // false
printf("True is %d\n", boolean_true);
printf("False is %d\n", boolean_false);
printf(boolean_true ? "true" : "false");
printf("\n");
printf(boolean_false ? "true" : "false");
return 0;
}
Output :
True is 1
False is 0
true
false
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h> // true와 false를 직접 문자로 넣어 사용 가능
int main()
{
bool bt = true;
bool bf = false;
printf("True is %d\n", bt);
printf("False is %d\n", bf);
return 0;
}
Output :
True is 1
False is 0
6.7 관계 연산자의 우선순위
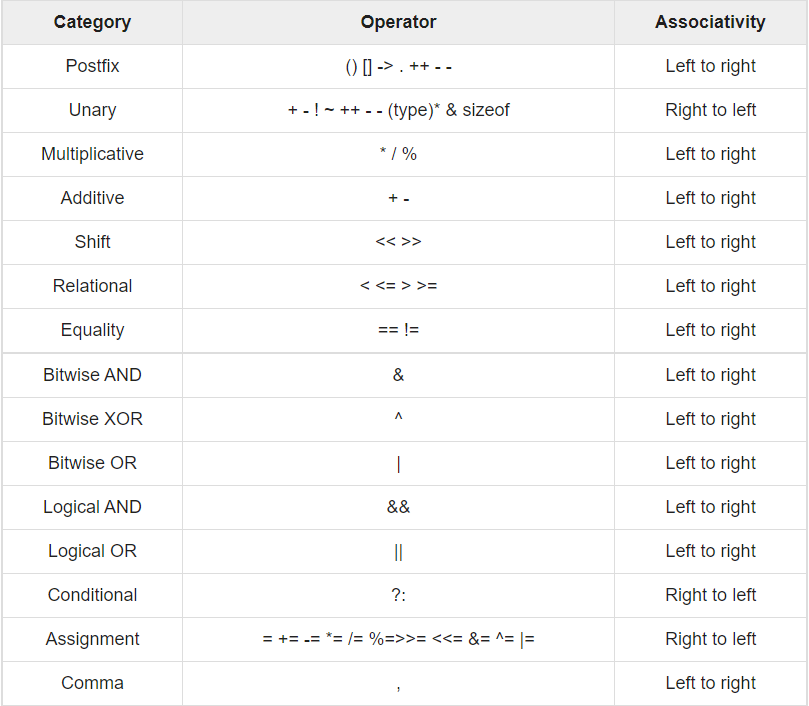
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 1, y = 2, z;
x > y + 2; // + 연산자가 > 연산자보다 우선순위가 높으므로
x > (y + 2); // 마치 y + 2에 괄호가 쳐져있듯이 계산
x = y > 2; // > 연산자가 = 연산자보다 우선순위가 높으므로
x = (y > 2); // 마치 y > 2에 괄호가 쳐져있듯이 계산
x != y == z; // != 와 == 는 우선순위가 동일하므로
(x != y) == z; // 왼쪽부터 계산
return 0;
}
6.8 for 루프 소개
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
/*
for (initialize ; test ; update)
statement
*/
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
printf("\n");
for (int j = 1; j <= 10; j++) // 초기값, 종료 조건, 증감값
printf("%d ", j);
return 0;
}- 실무에서는 거의 for문 사용 -> 편리하고 유연하게 사용 가능하기 때문
Output :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
6.9 for는 유연해요
- 아래처럼 다양한 방식 사용 가능
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 10; i > 0; i--)
printf("%d ", i);
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i += 8)
printf("%d ", i);
printf("\n");
for (char c = 'A'; c <= 'Z'; c++)
printf("%c ", c);
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i * i < 10; i++)
printf("%d ", i);
printf("\n");
for (int x = 1, y = 5; y <= 20; y = (++x * 3) + 10)
printf("%d ", x);
printf("\n");
for (double d = 100.0; d < 300; d *= 1.1)
printf("%f\n",d);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output :
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80 88 96
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
0 1 2 3
1 2 3
100.000000
110.000000
121.000000
133.100000
146.410000
161.051000
177.156100
194.871710
214.358881
235.794769
259.374246
285.311671
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, n = 2;
for (i = 2; n < 10;) {
n *= i;
printf("%d\n", n);
}
printf("\n");
i = 0;
for (printf("Let`s go!\n"); i != 7; scanf("%d", &i))
; // 입력받은 숫자가 7일때까지 반복
return 0;
}
Output :
4
8
16
Let`s go!
(1 입력)
(2 입력)
(6 입력)
(7 입력)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (;;) // while (1)과 동일
printf("Hello World ");
return 0;
}
Output :
Hello World 무한 출력
- 코드는 밋밋한, 기본적인게 좋음. 경쟁력은 알고리즘으로. 코딩에서 기교 부리지 말 것
강의 출처 : https://www.inflearn.com/course/following-c/dashboard
홍정모의 따라하며 배우는 C언어 - 인프런 | 강의
'따배씨++'의 성원에 힘입어 새롭게 개발된 C 언어로 시작하는 프로그래밍 입문 강의입니다. '따배씨'와 함께 프로그래밍 인생을 업그레이드 해보세요., 따라하며 배우는 C언어 '따배씨++'의 성원
www.inflearn.com