https://www.hmc.edu/lair/E190Q/labs.html
About Jaguar
- Dr Robot사의 4 Wheel Mobile Robot
- 실내/ 실외 주행이 가능하며, 험지 주행또한 가능
- 155mm의 Vertical Step, 110mm의 계단을 오를 수 있고 45도 경사 극복 가능
- 최대 속도 14km/h, 80W의 24V Motor
- 573mm * 615mm * 265mm, 20.5kg, 88mm의 지상고
- 정격 적재 중량 30kg, 최대 적재 가능 중량 50kg
- 802.11B/G Wireless Connection
- SDK, Data Protocol, Sample Code 포함, Microsoft Robotics Studio, Visual Studio, NI LabVIEW, MATLAB, Java, ROS 지원
- Jaguar`s Datasheet
- How to Connect
- "Jaguar Control' Program을 실행시키는 Remote Host Controller PC는 아래의 2가지 방법으로 Jaguar에 연결할 수 있다
- Network Cable : Robot on-board AP/Router에 연결 (WAN Port에 연결 X)
- Wireless : Host Controller PC를 Robot상의 Wireless AP/Router에 연결하기 위해선 Host PC의 Wireless setting을 아래의 Default Wireless Configuration Setting 대로 설정해야 함
- 본 글에서는 위의 방식들 중 자율주행을 위한 Wireless Connection 방식을 사용할 예정
- Pre-Configured Wireless 802.11B/G Router는 아래의 Pre-Setting을 가짐
- 802.11B/G는 Wifi 표준을 의미
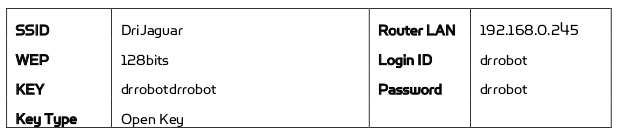
- Divice Default Network Setting은 아래와 같다
- Ethernet Module들은 Jaguar Platform에서 Serial - to Ethernet Mode로 configure되어있다
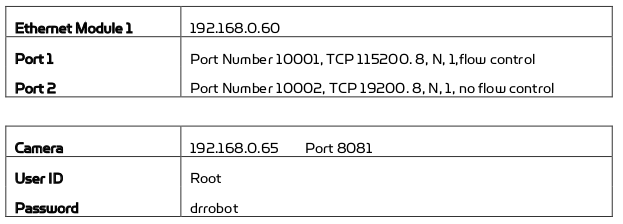
- Jaguar의 전원을 킨 후 'DriJaguar' Wifi에 접속 후 Password(drrobotdrrobot) 입력하여 Robot의 Router에 연결
- 이후 TCP Socket 연결을 통해 Motion Sensing Controller에 연결
- Server IP : 192.168.0.60
- Server Port : 10001
- TCP 통신 코드 (미완)
// This code sets up a TCP socket connection to the Motion sensing controller and checks for any errors during socket
// creation, address setup, and connection establishment
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
// Create a TCP socket using the 'socket' function
// Address family : AF_INET (IPv4)
// Socket Type : SOCK_STREM (TCP)
// Protocol : 0 (default protocol)
// socket function returns a file descriptor which represents the socket
int socket_client = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (socket_client == -1) {
std::cerr << "Failed to create socket." << std::endl;
return 1; // Display error message if the socket creation fails and exit the program
}
// Set the IP address and port number
std::string server_ip = "192.168.0.60";
int server_port = 10001;
// Set up the server address
// 'sockaddr_in' structure represents the server`s address
sockaddr_in server_address{}; // Structure describing an Internet socket address
server_address.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_address.sin_port = htons(server_port);
// 'inet_pton()' function converts the IP address from the string format to binary format
// and stores it in 'server_address.sin_addr'
// Detail : Convert from presentation format of an Internet number in buffer
// starting at CP to the binary network format and store result for
// interface type AF in buffer starting at BUF
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, server_ip.c_str(), &(server_address.sin_addr)) <= 0) {
std::cerr << "Invalid address or address not supported." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Connect to the server using 'connect()' function
// It takes the socket file descriptor(socket_client), server address structure, and size of the address sturcture as arguments
if (connect(socket_client, reinterpret_cast<sockaddr*>(&server_address), sizeof(server_address)) < 0) {
std::cerr << "Connection failed." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Connection successful! You can now send and receive data from the Motion sensing controller.
// Close the socket when you're done
close(socket_client);
return 0;
}- 연결 완료 후 Motor를 Control하고 Encoder Value를 받아오는 code 작성 필요
- 이후 I2C Protocol을 통해 IMU Module에 연결
- IC2 통신 코드 (미완)
// Tihs code sets up the I2C communication, configures the IMU, reads the
// desired sensor data, and displays it on the console.
#include <iostream>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
// Function to read a 16-bit signed integer from two consecutive registers
int16_t read16(int file, uint8_t address)
{
uint8_t highByte, lowByte;
highByte = lowByte = 0;
// Read the high byte
if (read(file, &highByte, sizeof(highByte)) != sizeof(highByte))
{
std::cerr << "Error reading high byte from I2C device" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// Read the low byte
if (read(file, &lowByte, sizeof(lowByte)) != sizeof(lowByte))
{
std::cerr << "Error reading low byte from I2C device" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// Combine the high and low bytes into a 16-bit signed integer
int16_t value = (highByte << 8) | lowByte;
return value;
}
int main()
{
// Open the I2C device file
int file = open("/dev/i2c-1", O_RDWR);
if (file < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Error opening I2C device" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Set the slave address of the IMU (GY-85 BMP085)
// The 'ioctl()' function perform the I/O control operation specified by REQUEST on FD(file).
// One argument may follow; its presence and type depend on REQUEST.
// Return value depends on REQUEST. Usually -1 indicates error.
if (ioctl(file, I2C_SLAVE, 0x77) < 0)
{
std::cerr << "Error setting I2C slave address" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Configure the IMU for Acceleration, Gyroscope, and Magnetic Field measurements
uint8_t configRegister = 0x20; // Configuration register address
uint8_t configValue = 0x0F; // Configuration value for enabling Acceleration, Gyroscope, and Magnetic Field measurements
if (write(file, &configRegister, sizeof(configRegister)) != sizeof(configRegister))
{
std::cerr << "Error writing to I2C device" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
if (write(file, &configValue, sizeof(configValue)) != sizeof(configValue))
{
std::cerr << "Error writing to I2C device" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// Read Acceleration data from the IMU
uint8_t accelRegister = 0x53; // Register address for Acceleration data
int16_t accelX = read16(file, accelRegister);
int16_t accelY = read16(file, accelRegister + 2);
int16_t accelZ = read16(file, accelRegister + 4);
// Read Gyroscope data from the IMU
uint8_t gyroRegister = 0x69; // Register address for Gyroscope data
int16_t gyroX = read16(file, gyroRegister + 8);
int16_t gyroY = read16(file, gyroRegister + 10);
int16_t gyroZ = read16(file, gyroRegister + 12);
// Read Magnetic Field data from the IMU
uint8_t magRegister = 0x1E; // Register address for Magnetic Field data
int16_t magX = read16(file, magRegister + 16);
int16_t magY = read16(file, magRegister + 18);
int16_t magZ = read16(file, magRegister + 20);
// Display the Acceleration, Gyroscope, and Magnetic Field data
std::cout << "Acceleration (X/Y/Z): " << accelX << " / " << accelY << " / " << accelZ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Gyroscope (X/Y/Z): " << gyroX << " / " << gyroY << " / " << gyroZ << std::endl;
std::cout << "Magnetic Field (X/Y/Z): " << magX << " / " << magY << " / " << magZ << std::endl;
// Close the I2C device file
close(file);
return 0;
}
- About IMU Module

https://ko.aliexpress.com/item/1005005237583197.html?_t=pvid%3Aa58c97f9-4c33-4df1-b714-5f6ba74b7191&afTraceInfo=1005005237583197__pc__pcBridgePPC__xxxxxx__1688489471&gatewayAdapt=glo2kor&pdp_npi=2%40dis%21KRW%21%E2%82%A99%2C531%21%E2%82%A96%2C667%21%21%21%21%21%402141005d16884894713333455efbda%2112000032317829508%21btf&spm=a2g0o.ppclist.product.mainProduct
AliExpress.com에 오신것을 환영합니다 로그아웃 회원가입 로그인 내 주문 내 코인 메시지 센터 결제 위시리스트 내 쿠폰
ko.aliexpress.com
- 로봇 내의 IMU Module (GY-85 BMP085, 9 DOF)
- ITG3205(Gyroscope) + ADXL345(Accelerometer) + HMC5883L(Magnetometry)
- 각 Sensor의 Datasheet
- 각 Sensor의 Output Registers
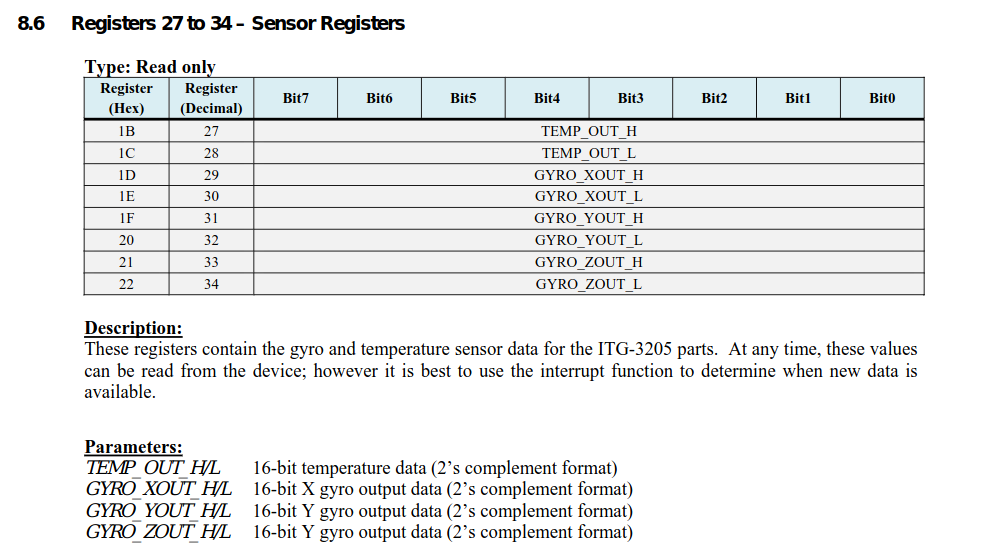
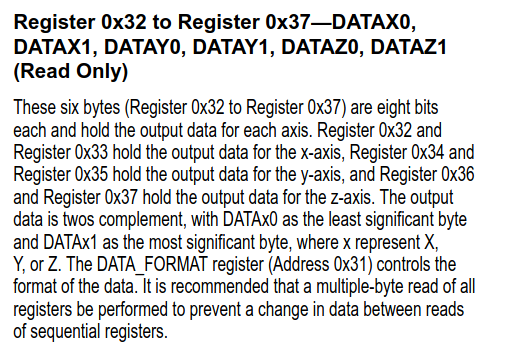

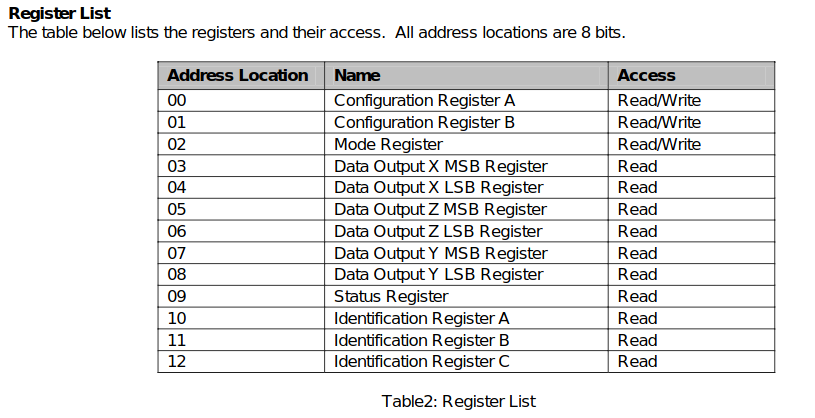
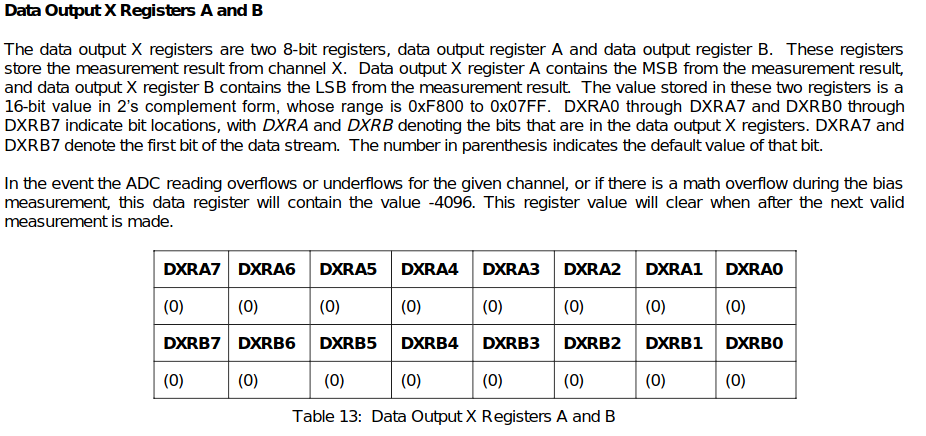
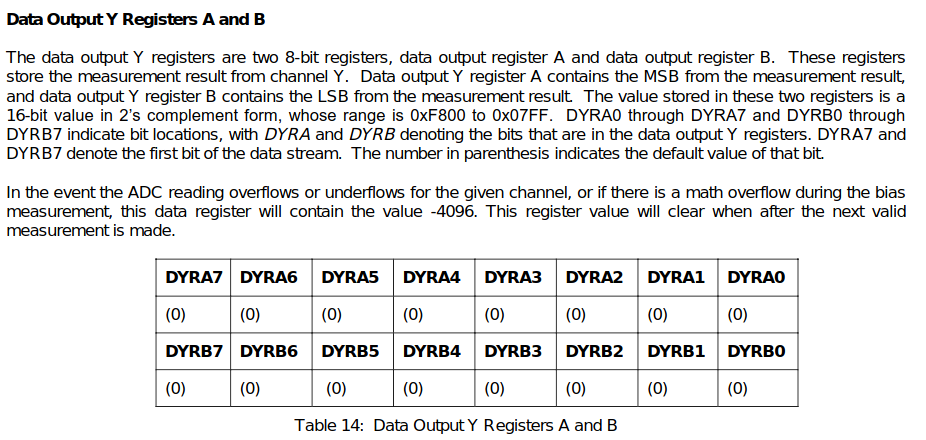
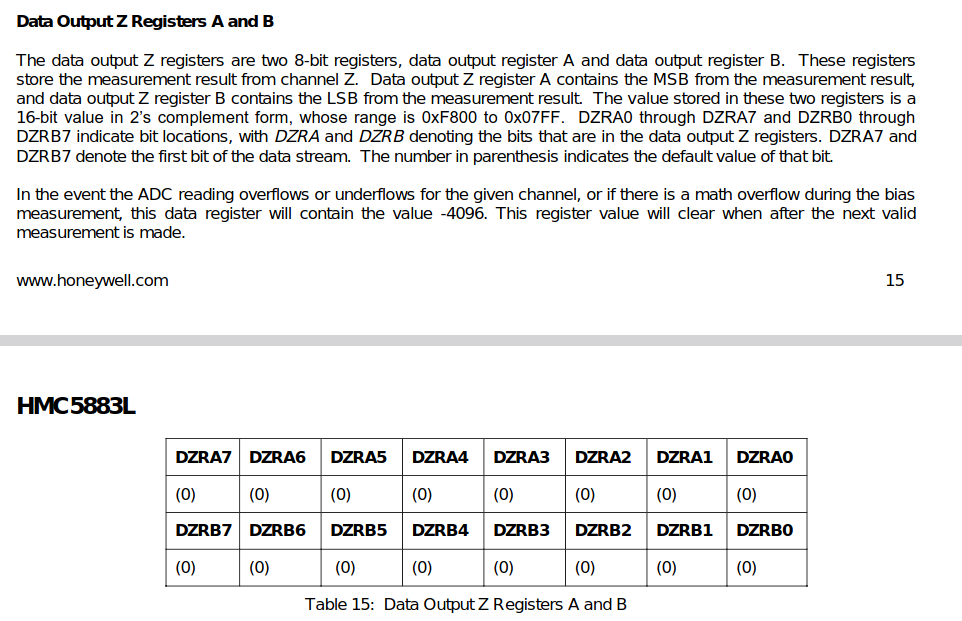
- Example Source
GitHub - madc/GY-85: Arduino implementation for GY-85 (ADXL345 accelerometer, ITG3200 gyroscope and HMC5883L magnetometer)
Arduino implementation for GY-85 (ADXL345 accelerometer, ITG3200 gyroscope and HMC5883L magnetometer) - GitHub - madc/GY-85: Arduino implementation for GY-85 (ADXL345 accelerometer, ITG3200 gyrosco...
github.com
GY-85 — A quick datasheet study
ADXL345 How it Works #arduSerie 34
medium.com
참고 자료 :
1) 통신 관련 내용
https://youngseong.tistory.com/181
https://youngseong.tistory.com/180
'Project > Jaguar 4X4 Human Tracking' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Jaguar 4x4 Human Tracking] 8/17 ~18 (0) | 2023.08.18 |
|---|---|
| [Jaguar 4x4 Human Tracking] 7/28 (0) | 2023.07.28 |
| 6/28 About NGIMU Protocol (미완) (0) | 2023.06.28 |


