1. 작품 개요
- 한국의 대표적 사회 문제들 중 하나는 고령 인구의 증가와 신생아 수 감소이며, 이로 인해 거동이 제한되는 고령 요양자나 입원 환자의 수는 증가하고 의료 인구는 감소될 것으로 예상됨
- 이러한 현상을 해결하는데 도움이 되고자 자동으로 배액을 수거 및 폐기하는 자율주행 로봇을 제작하기로 결정
2. System 구성
- OS : Ubuntu 18.04 - ROS Melodic
- Controller Board : Jetson Nano 2GB Developer Kit
- 사용 센서
- Motor : MDRobot - BL9N Series Motor (BLDC)
- Motor Driver : MD200T
- IMU : iAHRS (RB-SDA-v1)
- Lidar : RPLidar A1
- Depth Camera : RealSense D457
- rules file을 통해 각 센서들의 USB 포트에 대한 Symbolic Link를 생성하여 사용


2.1 Hardware 구성


- Robot이 너무 낮아서 사람의 눈에 띄지 않아 부딪히는 문제를 방지하고자 1m가 넘는 높은 구조를 설계


2.1.1. 구동부


- 구동부 1층에 motor, motor driver 배치
- Bracket을 통해 motor와 K9H 감속기 장착
- Bracket의 frame과의 연결부를 SLOT 처리해 좌우로 움직일 수 있도록 하여 belt의 tension을 원하는 수준으로 설정할 수 있도록 함

- Robot의 하중을 안정적으로 지지하기 위해 main frame 하단에 bearing housing을 이용하여 구동축 장착
- 95Φ의 철제 휠을 구동 휠로 사용하였으며, rim 부분에 고무 lining이 적용되어 실내주행간에 slip이 일어나지 않도록 함
- Frame 상단의 motor로부터 belt를 이용하여 동력 전달
2.1.2. 접속부

- 다수의 profile을 통한 접속부 뼈대 제작


- 배액 container에 접속하여 배액 수거 및 처리를 진행하기 위한 2 DOF 접속부 설계 및 제작



- SP(Socket - Plug) Coupler를 통한 접속 구조 설계
- 자율주행 구현 전 수동 조작을 통한 주행 test 진행
2.1.3. 전원 공급



- 24V 배터리를 통해 Motor Driver, CNC Shield에 전원 공급
- 12V 배터리를 통해 L298N에 전원 공급
- 5V 보조배터리 2개로 하나는 Jetson Nano의 동작 전원, 다른 하나는 USB 확장 허브에 추가 전력 공급
- 여러 센서들이 병렬로 연결되어 공급 전력 부족으로 인한 과전류 등의 문제를 방지하기 위함


2.2. Software 구성 : ROS 기반 자율주행 system 구성
2.2.1. Sensor 환경 구축
- Open Source를 활용하여 각 sensor 구동을 위한 ROS Package 사용
- IMU (iAHRS)


- Lidar (RPLidar A1)
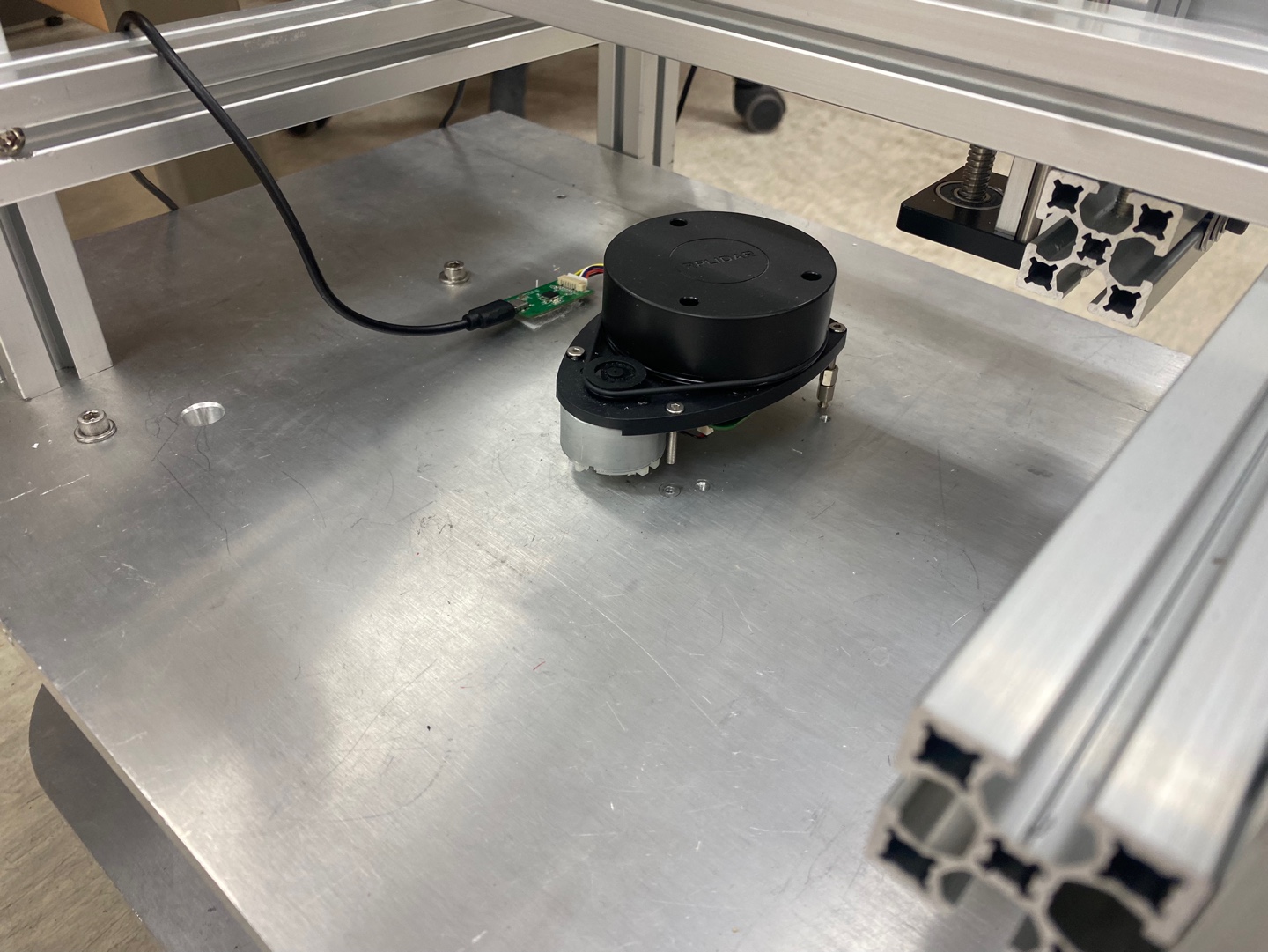
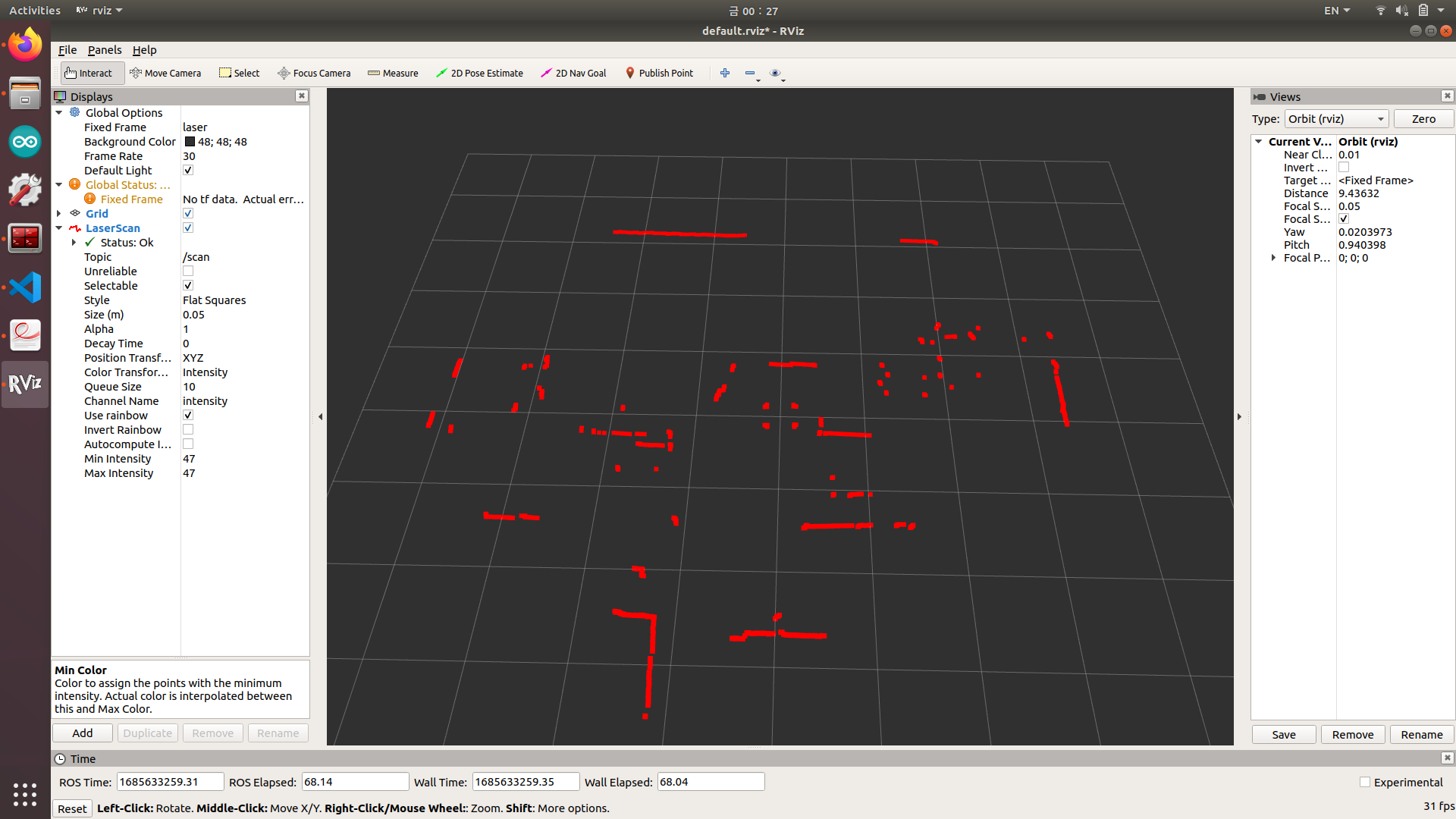
- Robot 상단 구조물 지지를 위해 profile 4개가 Lidar 주변을 통과하는 구조로 제작
- 해당 profile을 obstacle로 인식하여 주행에 방해가 될 것을 방지하기 위해 ROS laser_filters의 LaserScanAngularBoundsFilterInPlace filter를 활용하여 Lidar 기준 profile에 해당하는 angle을 제거 (radian 단위)
# scan_data_filter.yaml
scan_filter_chain:
- name: ProfileFrontLeft
type: laser_filters/LaserScanAngularBoundsFilterInPlace
params:
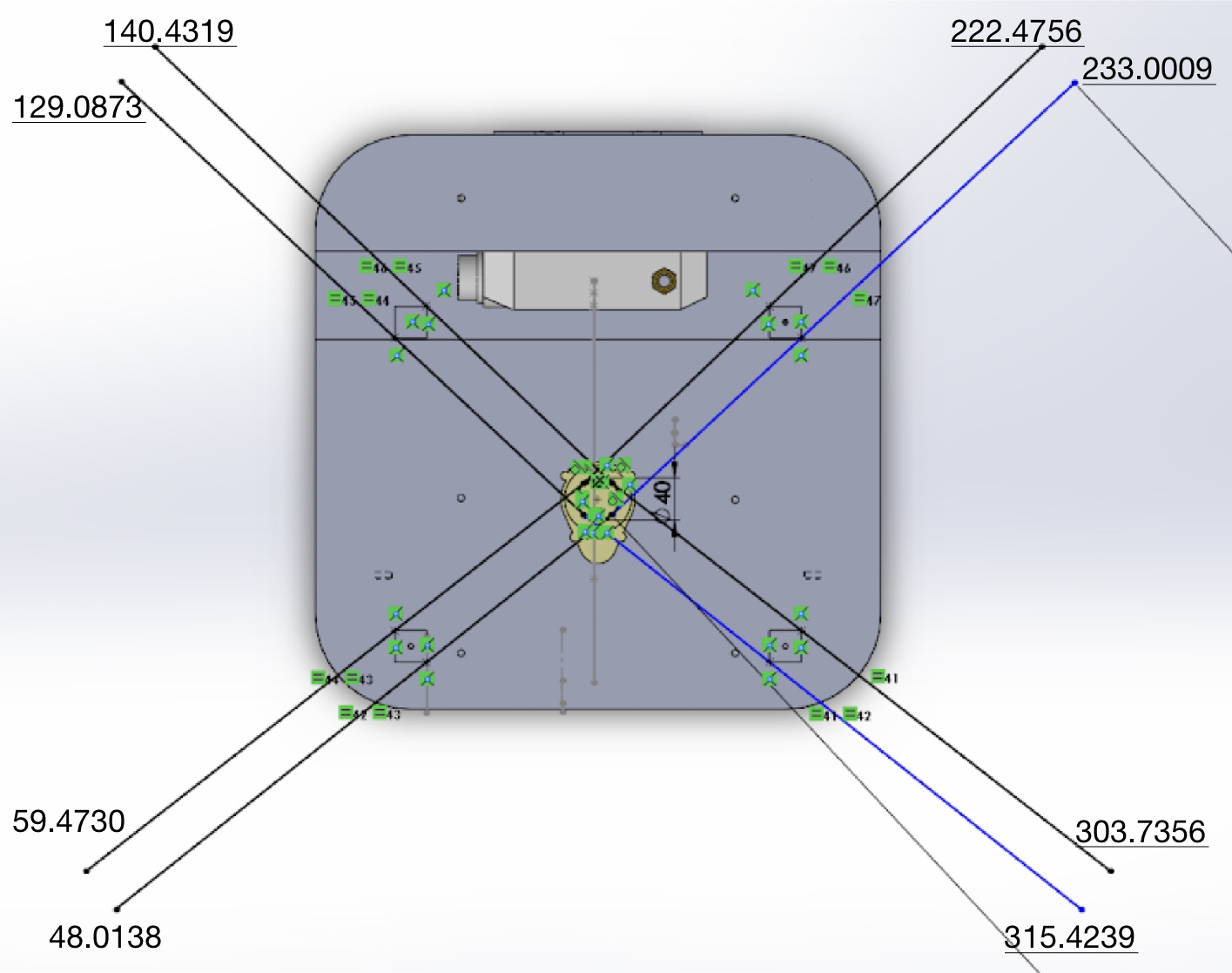
lower_angle: 0.838 # 48.0138
upper_angle: 1.038 # 59.4730
- name: ProfileBackLeft
type: laser_filters/LaserScanAngularBoundsFilterInPlace
params:
lower_angle: 2.253 # 129.0873
upper_angle: 2.451 # 140.4319
- name: ProfileBackRight
type: laser_filters/LaserScanAngularBoundsFilterInPlace
params:
lower_angle: -2.402 # 222.4756
upper_angle: -2.215 # 233.0009
- name: ProfileFrontRight
type: laser_filters/LaserScanAngularBoundsFilterInPlace
params:
lower_angle: -0.982 # 303.7356
upper_angle: -0.778 # 315.4239
- 확인 결과 profile에 의해 가려지는 영역은 아래와 같이 10도 내외의 넓지 않은 영역임을 확인
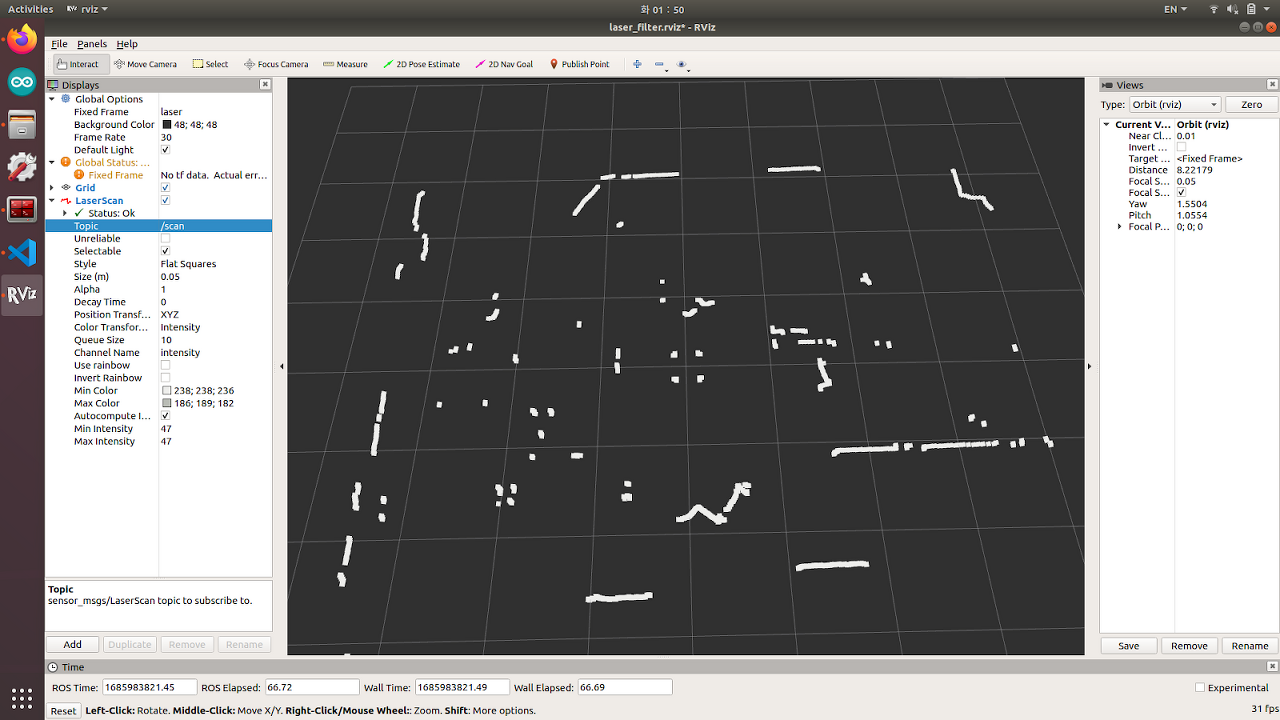

- Filter 적용 후 profile에 해당하는 중간부분의 장애물이 사라진 모습
- Intel RealSense D457


- 위 sensor들을 Jetson Nano에 연결 후 동시 구동을 위한 ROS launch file 생성
<!-- host.launch -->
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- Use this file to launch only sensors and motors at Embedded Board -->
<!-- This file should launched at ROS Host PC -->
<!-- Localization, EKF, Odometry Publisher, AMCL, Move_base node will be launched at remote PC using Master.launch -->
<!-- Transformation Configuration -->
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_link_to_laser" args="0.085 0 0.22 0 0 0 base_link laser 10" />
<node pkg="tf" type="static_transform_publisher" name="base_link_broadcaster" args="0 0 0.09 0 0 0 base_footprint base_link 10" />
<!-- Launch IMU(Iahrs) -->
<!-- Publish : /imu/data, TF to base_link -> laser -->
<param name="m_bSingle_TF_option" type="bool" value="true" />
<node pkg="iahrs_driver" type="iahrs_driver" name="iahrs_driver" output="screen" />
<!-- Launch Lidar(RPLidarA1) -->
<!-- Publish : /scan -->
<node name="rplidarNode" pkg="rplidar_ros" type="rplidarNode" output="screen">
<param name="serial_port" type="string" value="/dev/ttyRPLidar"/>
<param name="serial_baudrate" type="int" value="115200"/>
<param name="frame_id" type="string" value="laser"/>
<param name="inverted" type="bool" value="false"/>
<param name="angle_compensate" type="bool" value="true"/>
</node>
<!-- Add laser_filter -->
<node pkg="laser_filters" type="scan_to_scan_filter_chain" name="laser_filter" output="screen">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find navstack)/param/scan_data_filter.yaml"/>
</node>
<!-- Launch 3D Depth Camera(Realsense D457) -->
<include file="$(find realsense2_camera)/launch/rs_rgbd.launch"/>
<!-- Launch Motor Driver(MD200T) -->
<!-- Subscribe: /cmd_vel -->
<!-- Publish : /right_ticks, /left_ticks -->
<node pkg="md" type="md_robot_node" name="md_robot_node" output="screen">
<param name = "use_MDUI" value = "0"/> <!-- 0: not use MDUI, 1: use MDUI -->
<param name = "wheel_radius" value = "0.095"/> <!-- unit: meter -->
<param name = "wheel_length" value = "0.047"/> <!-- unit: meter -->
<param name = "motor_pole" value = "8"/>
<param name = "reduction" value = "15"/>
<param name = "reverse_direction" value = "0"/> <!-- 0: forward, 1: reverse -->
<param name = "maxrpm" value = "3000"/> <!-- unit: RPM -->
<param name = "motor_posi" value = "0"/> <!-- motor pisition 0: hall sensor, 1: encoder -->
<param name = "encoder_PPR" value = "16384"/> <!-- if use encoder position, encoder PPR -->
<param name = "position_proportion_gain" value = "20"/> <!-- reference PID 203(PID_GAIN) -->
<param name = "speed_proportion_gain" value = "50"/> <!-- reference PID 203(PID_GAIN) -->
<param name = "integral_gain" value = "1800"/> <!-- reference PID 203(PID_GAIN) -->
<param name = "slow_start" value = "300"/> <!-- unit: RPM. Set Velocity -->
<param name = "slow_down" value = "300"/> <!-- unit: RPM -->
</node>
</launch>
2.2.2. 접속부 인식 및 제어
- Object Tracking
- Intel RealSense D457을 통한 Object Tracking을 통해 접속 위치 인식
- HSV값을 조절하여 찾고자 하는 Object를 특정할 수 있음
- 더 수월한 RGB값 인식을 위해 접속 위치를 빨간색으로 덮음

- Arduino Mega + CNC Shield + A4988 Step Motor Driver + L298N Motor Driver 를 활용한 제어를 통해 수동 접속 구현
- CNC Shield + A4988 : Z축 Actuator
- L298N : Y축 Actuator

#include <Stepper.h> // Library to use Stepper Motor
#define EN 8
const int stepPin = 2; // X.STEP Motor's direction control. Motor moves one step by pulse sent to this pin
const int dirPin = 5; // X.DIR Motor's Rotation Direction Control
const int degree_per_revolition = 200;
// Y Direction Actuator Connection
const int enA = 52; // Motor's PWM Input Pin. Set the motor's speed by this pin's value
const int in1 = 50; // Set Motor's Direction
const int in2 = 48; // Set Motor's Direction
bool motorRunning = false; // Variable to track if the motor is currently running
unsigned long currentMicros = 0;
unsigned long previousMicros = 0;
unsigned long periodMicros = 0;
int pwmFrequency = 100; // PWM frequency in Hz
int pwmDutyCycle = 255; // PWM duty cycle (0-255) for speed control
const int sw = 22;
char sw_state = HIGH;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set all pins to Output related to Z Actuator
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(EN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(sw, INPUT);
digitalWrite(EN, LOW);
// Set all pins to Output related to Y Actuator
pinMode(in1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enA, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) { // Set to read Keyboard Input
char input = Serial.read();
Serial.print("Input : ");
Serial.println(input);
/* Z Actuator Control */
if (input == 'q') {
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH); // Set Z Actuator to move Upward
motorRunning = true; // Start the motor
}
else if (input == 'e') {
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW); // Set Z Actuator to move Downward
motorRunning = true; // Start the motor
}
else if (input == 'w') {
motorRunning = false; // Stop Z Actuator
}
/* Y Actuator Control */
else if (input == 'a') { // Set Y Actuator to move Forward
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
}
else if (input == 'd') { // Set Y Actuator to move Backward
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
}
else if (input == 's') { // Stop Y Actuator
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
}
/* Stop all the Actuators */
else if (input == 'x') {
motorRunning = false;
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
}
}
sw_state = digitalRead(sw);
if(sw_state == LOW){
Serial.println("Z direction Acutator reached to top point");
motorRunning = false;
}
/* Set Z Actuator */
if (motorRunning) {
// 1.8 degrees per 1 revolution
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(800); // Set Z Actuator's speed
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(800);
}
/* Set Y Actuator speed using software PWM */
currentMicros = micros();
periodMicros = 1000000 / pwmFrequency;
if (currentMicros - previousMicros >= periodMicros) {
previousMicros = currentMicros;
analogWrite(enA, pwmDutyCycle);
}
}- CNC Shield가 Arduino의 모든 PWM pin을 사용하고 있어 Software PWM을 통해 Y축 Actuator의 속도 설정
2.2.3. Navigation Stack 구성
- Navigation Stack : Robot을 현재 위치에서 목표 위치까지 움직이는 과정인 Navigation 수행을 위해 구성된 Software의 집합
- 세부 구성 요소는 다음과 같다
- TF (Transformation) 구성 : 서로 다른 Coordinate Frame에서 얻어지는 sensor data들을 Robot의 회전 중심점인 'base_link'에 통일시키기 위해 TF 정의


- EKF(Extended Kalman Filter)를 통해 Motor의 Encoder값과 IMU 센서의 data를 fusion
- Fusion한 data를 통해 Odometry data 생성 후 robot의 위치 추정
- Odometry란 '주행 기록계' 라는 뜻으로, 시간에 따른 출발 지점으로부터의 상대적인 위치 변화를 추정
- Global / Local Costmap 구성
- Costmap : 각 Cell들이 특정한 값(cost)를 부여받는 Grid Map. 값이 클수록 robot과 obstacle 사이의 거리가 가까움을 의미. 일반적으로 각 Cell들은 0~255 사이의 binary 값을 가짐
- Global Costmap : SLAM을 통해 얻은 Static Map으로부터 만들어지며 새로운 obstacle이 나타난다거나 하는 등의 환경이 바뀌더라도 변하지 않음
- Local Costmap : Robot의 sensor data로부터 실시간으로 obstacle에 대한 정보를 얻으며 만들어짐. Local Planner가 이를 토대로 odometry와 laser data를 계속 확인하며 충돌이 없는 local plan을 선택함



- Base Contoller Node 구성
- Base Controller는 Navigation 수행을 위해 robot의 base coordinate를 기준으로 한 Velocity Command를 Motor에 적합한 Command로 변환하는 역할을 수행
- DWA(Dynamic Window Approach)를 Base Local Planner로 선택
- Base Local Planner : Robot의 base controller로 보내진 Velocity Command를 계산하는 Package로, Global Plan을 계산하고 실행하기 위한 여러 Algorithm들을 제공
- DWA algorithm은 이동체의 velocity, direction 및 sensor data로부터 얻는 obstacle과의 거리를 토대로 최적의 linear velocity와 angular velocity를 도출하여 obstacle을 회피하고 목적지에 도달한다.
- 즉 Map(위치 기반)을 Velocity Search Space(속도 탐색 영역)으로 변환하여 obstacle을 회피하며 목표지점까지 다다를 수 있는 최적의 velocity를 선정한다
- AMCL (Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization) Node 구성
- Localization : 주어진 Map상에서의 robot의 위치를 추적하는 과정
- AMCL : Particle Filter를 통해 Localization을 진행하는 MCL에서 적은 수의 sample 사용을 통해 수행 시간을 줄여 real-time성을 높인 algorithm
- 2D Map 상에서의 robot의 초기 추정 위치가 부여되면 XY 좌표 평면상에 robot의 위치를 확률적으로 나타낸 Particle의 분포를 sensor data를 기반으로 update해가며 robot의 위치를 추즉한다
- 이 과정을 위해 AMCL node는 TF, 각 sensor들의 계측값, Map 등의 data를 수신받아야 한다
- Move Base Node 구성
- Move Base Node는 Navigation을 수행하는 과정에서 발생하는 모든 요소들을 이어주는, Navigation Stack에서 매우 중요한 요소 중 하나
- 충돌 위험이 없는 path를 계획하는데 중요한 역할을 한다
- Jetson Nano에서 Motor Driver, IMU, Lidar를 동시 구동시키는 launch file(host.launch) 실행
- Remote PC에서 해당 센서값들을 통해 SLAM, Navigation을 진행할 수 있는 launch file 구성 후 실행
<!-- master.launch -->
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- Use this file to launch Map server, Odometry Publisher, EKF, AMCL and Move_base Node -->
<!-- This file should launched at ROS Master PC -->
<!-- Map File -->
<arg name="map_file" default="/home/lim/catkin_ws/maps/capstone.yaml"/>
<!-- Map Server -->
<!-- Publish: /map, /map_metadata -->
<node pkg="map_server" name="map_server" type="map_server" args="$(arg map_file)" />
<!-- Initial Pose and Goal Publisher -->
<!-- Publish: /initialpose, /move_base_simple/goal -->
<!-- Launch Rviz -->
<node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="rviz" args="-d /home/lim/catkin_ws/rviz_config/navigation.rviz">
</node>
<!-- Wheel Odometry Publisher -->
<!-- Subscribe: /right_ticks, /left_ticks, /initial_2d -->
<!-- Publish: /odom_data_euler, /odom_data_quat -->
<node pkg="localization_data" type="ekf_odom_pub" name="ekf_odom_pub">
</node>
<!-- Launch OpenCV Objective Tracking
<node pkg="opencv_object_tracking" type="object_filter" name="object_filter">-->
<!-- Subscribe: /initialpose, /move_base_simple/goal -->
<!-- Publish: /initial_2d, /goal_2d -->
<!-- Launch rviz_click_to_2d node -->
<node pkg="localization_data" type="rviz_click_to_2d" name="rviz_click_to_2d">
</node>
<!-- Extended Kalman Filter from robot_pose_ekf Node-->
<!-- Subscribe: /odom, /imu_data, /vo -->
<!-- Publish: /robot_pose_ekf/odom_combined, TF to odom -> base_footprint -->
<remap from="odom" to="odom_data_quat" />
<remap from="imu_data" to="imu/data" />
<node pkg="robot_pose_ekf" type="robot_pose_ekf" name="robot_pose_ekf">
<param name="output_frame" value="odom"/>
<param name="base_footprint_frame" value="base_footprint"/>
<param name="freq" value="30.0"/>
<param name="sensor_timeout" value="1.0"/>
<param name="odom_used" value="true"/>
<param name="imu_used" value="true"/>
<param name="vo_used" value="false"/>
<param name="gps_used" value="false"/>
<param name="debug" value="false"/>
<param name="self_diagnose" value="false"/>
</node>
<!-- Launch AMCL node for differential drive robots for Localization -->
<!-- Subscribe:/scan, /tf, /initial_pose, /map -->
<!-- Publish: /amcl_pose, /particlecloud, /tf -->
<include file="$(find navstack)/launch/amcl.launch"/>
<!-- Move Base Node -->
<!-- Subscribe: /move_base_simple/goal -->
<!-- Publish: /cmd_vel -->
<include file="$(find navstack)/launch/move_base.launch"/>
</launch>

3. 자율주행 구현
3.1. SLAM
- Hector / Cartographer SLAM을 통한 실내 Mapping 진행
- Hector SLAM은 Odometry 정보를 필요로 하지않아 Lidar 만으로 Mapping 가능
- Cartographer SLAM은 Odometry 정보를 토대로 비교적 정밀한 Mapping 가능


3.2. Navigation
- 앞서 SLAM을 통해 얻은 map상에서의 Navigation 진행
- AMCL을 통한 localization 진행
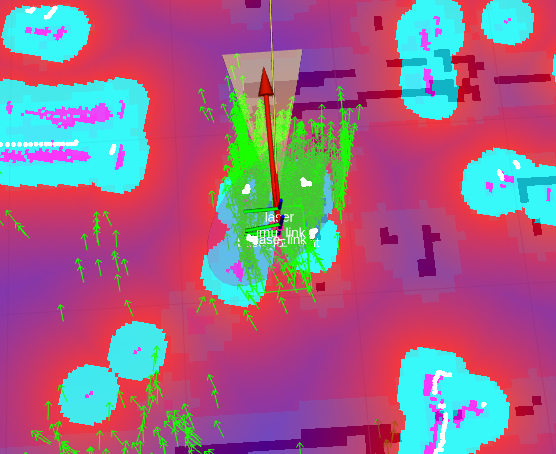


- Particle 수렴 후 robot에 목표 지점 부여

- DWA Local Planner를 통해 장애물을 회피할 수 있는 경로 생성 후 이동
- AMCL, DWA, Move Base node등의 parameter 최적화가 이뤄지지 않아 원활한 Navigation 구현이 되지 못하는 모습
- 추후 과제
- 현재 모터 드라이버가 고장난 상태 : 수리 or 새로 구매 필요
- 엔코더 값 수정 필요
- 배액 주머니 컨테이너의 접속부를 인식시킬 방안 탐색 필요
- 배액 폐기를 위한 구조 제작
- 여러 알고리즘의 parameters 수정을 통한 원활한 Navigation 구현 + TEB 등의 다른 Local Planner 적용
Source Code : https://github.com/YoungSeong98/Project_KUSMO
GitHub - YoungSeong98/Project_KUSMO
Contribute to YoungSeong98/Project_KUSMO development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
Project 진행 과정 : https://youngseong.tistory.com/category/KUSMO
'KUSMO' 카테고리의 글 목록
youngseong.tistory.com
'Project > KUSMO' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [KUSMO] 7/21 (0) | 2023.07.24 |
|---|---|
| [KUSMO] 6/27 (0) | 2023.06.27 |
| [KUSMO] 6/5~7 (0) | 2023.06.07 |
| [KUSMO] 6/4 Arduino Symbolic Link 생성, laser_filters를 통한 프로파일 제거 (0) | 2023.06.04 |
| [KUSMO] 5/31 (0) | 2023.05.31 |


